In Top Academic Journals
Neutron star smashup 'transforms' our understanding

Galaxy NGC 4993, about 130 million light-years from Earth
Paris - AFP
For the first time, scientists have witnessed the cataclysmic crash of two ultra-dense neutron stars in a galaxy far away, and concluded that such impacts forged at least half the gold in the Universe.
Shockwaves and light flashes from the collision travelled some 130 million light-years to be captured by Earthly detectors on August 17, excited teams revealed at press conferences held around the globe on Monday as a dozen related science papers were published in top academic journals.
"We witnessed history unfolding in front of our eyes: two neutron stars drawing closer, closer... turning faster and faster around each other, then colliding and scattering debris all over the place," co-discoverer Benoit Mours of France's CNRS research institute told AFP.
The groundbreaking observation solved a number of physics riddles and sent ripples of excitement through the scientific community.
Most jaw-dropping for many, the data finally revealed where much of the gold, platinum, uranium, mercury and other heavy elements in the Universe came from.
Telescopes saw evidence of newly-forged material in the fallout, the teams said -- a source long suspected, now confirmed.
"It makes it quite clear that a significant fraction, maybe half, maybe more, of the heavy elements in the Universe are actually produced by this kind of collision," said physicist Patrick Sutton, a member of the US-based Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) which contributed to the find.
Neutron stars are the condensed, burnt-out cores that remain when massive stars run out of fuel, blow up, and die.
Typically about 20 kilometres (12 miles) in diameter, but with more mass than the Sun, they are highly radioactive and ultra-dense -- a handful of material from one weighs as much as Mount Everest.
- 'Too beautiful' -
It had been theorised that mergers of two such exotic bodies would create ripples in the fabric of space-time known as gravitational waves, as well as bright flashes of high-energy radiation called gamma ray bursts.
On August 17, detectors witnessed both phenomena, 1.7 seconds apart, coming from the same spot in the constellation of Hydra.
"It was clear to us within minutes that we had a binary neutron star detection," said David Shoemaker, another member of LIGO, which has detectors in Livingston, Louisiana and Hanford, Washington.
"The signals were much too beautiful to be anything but that," he told AFP.
The observation was the fruit of years of labour by thousands of scientists at more than 70 ground- and space-based observatories on all continents.
Along with LIGO, they include teams from Europe's Virgo gravitational wave detector in Italy, and a number of ground- and space-based telescopes including NASA's Hubble.
"This event marks a turning point in observational astronomy and will lead to a treasure trove of scientific results," said Bangalore Sathyaprakash from Cardiff University's School of Physics and Astronomy, recalling "the most exciting of my scientific life."
"It is tremendously exciting to experience a rare event that transforms our understanding of the workings of the Universe," added France Cordova, director of the National Science Foundation which funds LIGO.
The detection is another feather in the cap for German physicist Albert Einstein, who first predicted gravitational waves more than 100 years ago.
- Something 'fundamental' -
Three LIGO pioneers, Barry Barish, Kip Thorne and Rainer Weiss, were awarded the Nobel Physics Prize this month for the observation of gravitational waves, without which the latest discovery would not have been possible.
The ripples have been observed four times before now -- the first time by LIGO in September 2015. All four were from mergers of black holes, which are even more violent than neutron star crashes, but emit no light.
The fifth and latest detection was accompanied by a gamma ray burst which scientists said came from nearer in the Universe and was less bright than expected.
"What this event is telling us is that there may be many more of these short gamma ray bursts going off nearby in the Universe than we expected," Sutton said -- an exciting prospect for scientists hoping to uncover further secrets of the Universe.
Among other things, it is hoped that data from neutron star collisions will allow the definitive calculation of the rate at which the cosmos is expanding, which in turn will tell us how old it is and how much matter it contains.
"With these observations we are not just learning what happens when neutron stars collide, we're also learning something fundamental about the nature of the Universe," said Julie McEnery of the Fermi gamma ray space telescope project.
Source: AFP
With Job Cuts, China Deal
France's Carrefour revamps operations
Paris - Emiratesvoice
France's Carrefour group said Tuesday it is overhauling its business in a transformation plan involving thousands of job cuts, a product revamp and new partnerships in China. Carrefour, which was the world'sTo partake in Beiteddine Festivals
Singer Bruni arrives in Beirut Sunday evening
Beirut - NNA
French renowned singer and supermodel, Carla Bruni, is expected to arrive this evening at Rafic Hariri International Airport in Beirut, accompanied by her husband, former French President Nicolas Sarkozy. BruniIn France
Microsoft to open 4 data centres
Paris - Emiratesvoice
Microsoft is to open 4 data storage centers in France to meet strong customer demand for cloud computing, the head of the software giant's French operations told the Agence France-Presse onIn Olympic Spotlight
'Friendly and kind' N. Korean skaters
Taipei - Emiratesvoice
North Korea's figure skaters Ryom Tai-Ok and Kim Ju-Sik are "friendly and kind and a little bit shy", South Korea's Kim Kyueun said Tuesday ahead of their hugely anticipated Olympic appearance. The skater is competing with her partner Alex Kam in theFor $11.6 Bn
Sanofi buys US haemophilia treatment
Paris - Emiratesvoice
French pharmaceutical firm Sanofi said Monday it had reached an agreement to purchase US biotech company Bioverativ, which specialises in treatments for haemophilia and rare blood disorders, for $11.6 billion. Sanofi's chief executive Olivier Brandicourt said the acquisition "enhances its presence in specialtyParis show pays homage
to 'eternal style' of late Alaia
Paris - Emiratesvoice
Two months after legendary designer Azzedine Alaia's sudden death plunged the fashion world into mourning, an exhibition in homage to the "King of Cling" opens Monday in his studios in Paris. The Tunisian-born designer, renowned for the way his clothes hugged the body, died suddenly in November aged 82, reportedly of heart failure after falling down the stairs at his home. The diminutive maverick, who ignored fashion week convention by showing when and where he wanted, in July produced his first couture collection in six years to rapturous reviews. Now some of his most iconic dresses are going on display in the glass-roofed gallery next to his studio and home in the Marais district where he used to show his creations. It includes the dress worn by supermodel Naomi Campbell, his longtime friend and muse, when she ledMaintained and developed by Arabs Today Group SAL.
All rights reserved to Arab Today Media Group 2025 ©
Maintained and developed by Arabs Today Group SAL.
All rights reserved to Arab Today Media Group 2025 ©






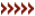














Send your comments
Your comment as a visitor